Design Considerations for 4 Bedroom Slab House Plans
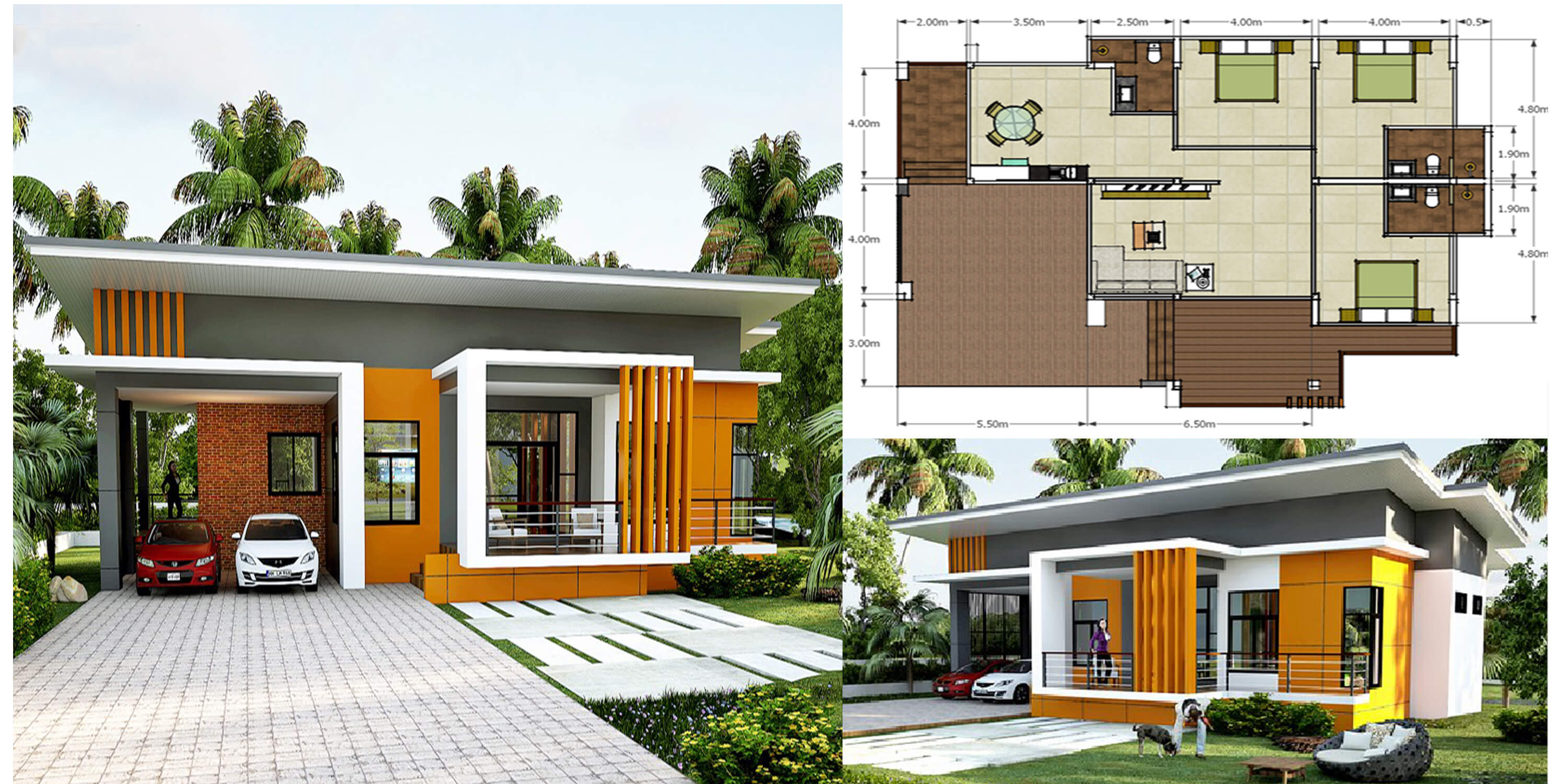

A 4 bedroom slab house plan offers a spacious and modern living experience, but it’s crucial to consider specific design elements to ensure comfort, functionality, and long-term satisfaction.
Insulation and Ventilation
Proper insulation and ventilation are essential for maintaining a comfortable temperature year-round in a slab home. Slab foundations can be susceptible to heat gain in the summer and heat loss in the winter. Effective insulation helps minimize these temperature fluctuations, reducing energy consumption and creating a more pleasant living environment. Here are some key considerations:
- Insulation: Consider using high-performance insulation materials like spray foam or rigid foam boards for the slab itself and the surrounding walls. This will create a thermal barrier, preventing heat transfer and maintaining a comfortable indoor temperature.
- Ventilation: Adequate ventilation is crucial for removing moisture and stale air, preventing mold growth and ensuring good air quality. Incorporate a well-designed ventilation system, including exhaust fans in bathrooms and kitchens, and consider using attic fans or whole-house ventilation systems for optimal air circulation.
Maximizing Space and Functionality
A 4 bedroom slab home presents ample space, but maximizing its functionality requires thoughtful planning. Here are some tips for creating a comfortable and efficient layout:
- Bedroom Sizes: While each bedroom should be comfortable, prioritize the master suite for ample space, including a walk-in closet and a private bathroom. This provides a relaxing retreat for the homeowners.
- Closet Space: Maximize closet space by incorporating built-in shelves and drawers. Consider using sliding doors for closets to save space, especially in smaller bedrooms.
- Shared Living Areas: Design a spacious and inviting living room, dining room, and kitchen. Consider open-concept layouts that connect these areas, creating a sense of flow and maximizing natural light.
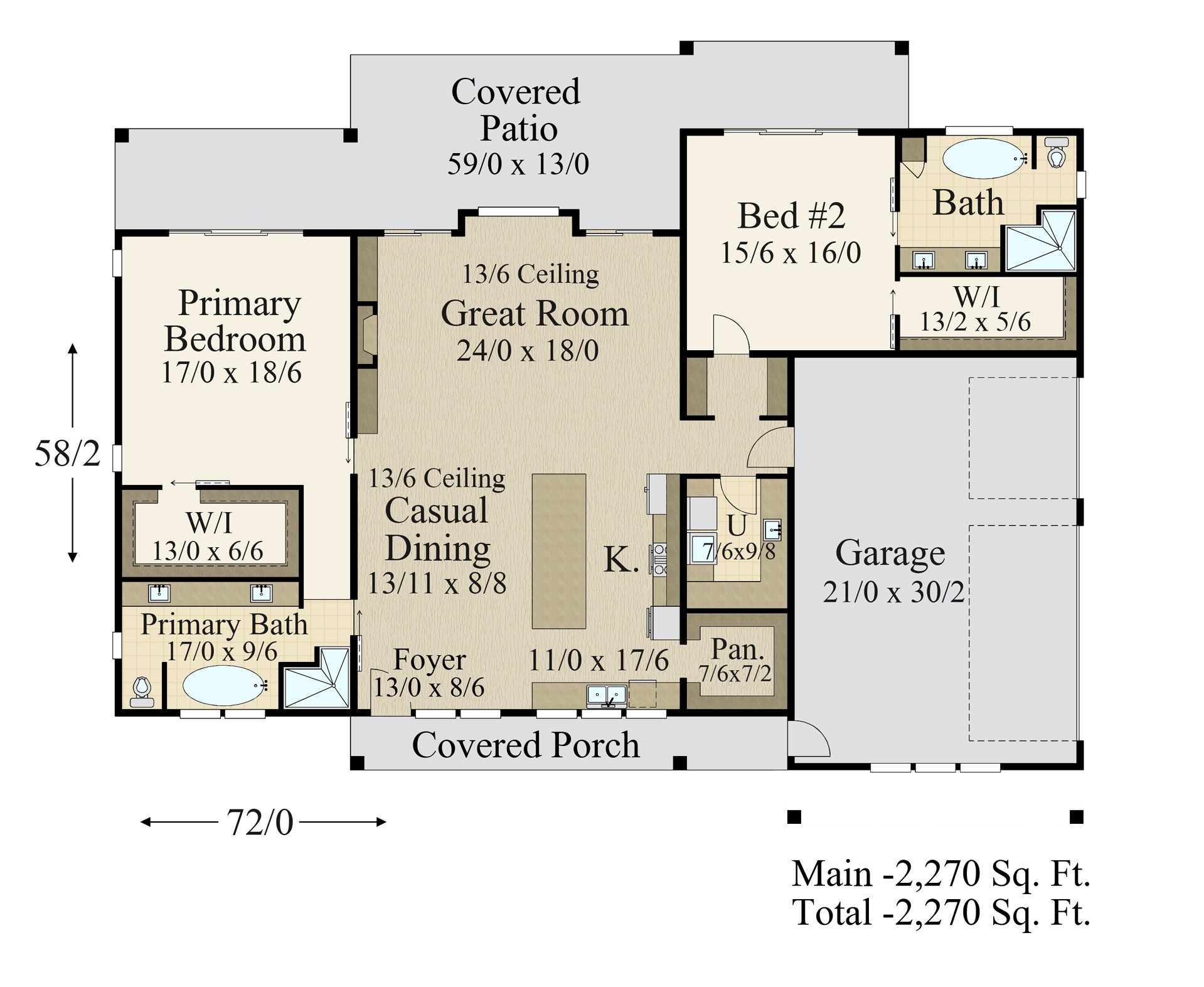
Sample Floor Plan
Here’s a sample floor plan for a 4 bedroom slab house, incorporating features for comfortable living:
- Entryway: A welcoming entryway with a coat closet provides a buffer between the outdoors and the main living area.
- Living Room: A spacious living room with large windows for natural light, a fireplace for ambiance, and ample seating for gatherings.
- Kitchen: A well-equipped kitchen with a large island for meal preparation and informal dining, ample cabinet and counter space, and a pantry for storage.
- Dining Room: A formal dining room adjacent to the kitchen for larger gatherings.
- Bedrooms: Three bedrooms, each with a closet and access to a shared bathroom.
- Master Suite: A spacious master suite with a walk-in closet, a private bathroom, and a separate sitting area.
- Laundry Room: A dedicated laundry room with washer and dryer hookups, cabinets for storage, and a sink.
Building a 4 Bedroom Slab House: 4 Bedroom Slab House Plans
Building a 4-bedroom slab house is a significant undertaking, requiring careful planning, meticulous execution, and adherence to local building codes. This comprehensive guide will walk you through the process, from foundation construction to final finishes, providing insights into selecting the right materials and contractors for a successful project.
Foundation Construction
The foundation is the bedrock of your home, and its integrity is paramount for a stable and safe structure. Here’s a breakdown of the process:
- Site Preparation: The first step involves clearing the construction site of debris, vegetation, and any obstacles. This ensures a level and stable foundation base.
- Excavation: The excavated area should be deeper than the frost line, preventing soil movement during freeze-thaw cycles. The depth is determined by local building codes and the climate of the region.
- Compacted Base: A layer of compacted gravel or crushed stone is placed over the excavated area, providing drainage and support for the concrete slab.
- Forms: Wooden or metal forms are erected around the perimeter of the slab, creating a mold for the concrete pour. The forms must be level and sturdy to ensure a smooth and even slab.
- Rebar and Wire Mesh: Reinforcing steel bars (rebar) and wire mesh are embedded within the concrete, adding strength and preventing cracking. The placement and spacing of rebar are specified by local building codes.
- Concrete Pour: The concrete is poured into the forms, ensuring proper compaction and level distribution. It’s essential to use a high-quality concrete mix that meets the requirements for residential construction.
- Curing: The concrete needs to cure properly, which involves maintaining moisture and temperature control. This process typically takes several days, allowing the concrete to gain strength.
Framing and Roofing
Once the foundation has cured, the framing and roofing process can begin. This involves constructing the walls and roof of the house, providing the structural support for the entire building.
- Wall Framing: Wooden studs are erected at 16-inch intervals, creating the framework for the walls. These studs are typically made of pressure-treated lumber, which resists moisture and decay.
- Roof Framing: The roof framing consists of rafters, joists, and sheathing. The rafters support the weight of the roof and are typically made of dimensional lumber. The joists provide support for the roof deck, and the sheathing creates a solid surface for the roofing material.
- Sheathing: Plywood or OSB sheathing is attached to the walls and roof framing, providing a solid surface for siding, roofing, and insulation.
- Insulation: Insulation is installed within the walls and roof, reducing heat loss and improving energy efficiency. The type and thickness of insulation are determined by local building codes and the climate of the region.
- Roofing: The roofing material is installed over the sheathing, providing weatherproofing and protection for the house. Common roofing materials include asphalt shingles, metal roofing, and tile roofing.
Plumbing and Electrical
Plumbing and electrical systems are essential for a functional and safe home. These systems need to be installed carefully and inspected to ensure compliance with local building codes.
- Plumbing: Plumbing pipes are installed within the walls and under the floor, carrying water to fixtures and appliances. The plumbing system includes water supply lines, drain lines, and vent lines.
- Electrical Wiring: Electrical wiring is installed within the walls and ceiling, providing power to outlets, lights, and appliances. The electrical system includes circuit breakers, grounding wires, and conduit.
Interior and Exterior Finishes
Once the framing, plumbing, and electrical work are complete, the focus shifts to the interior and exterior finishes. These finishes enhance the aesthetics and functionality of the home.
- Siding: Exterior siding protects the walls from the elements and provides a finished look. Common siding materials include vinyl siding, wood siding, and brick siding.
- Windows and Doors: Windows and doors provide natural light, ventilation, and access to the home. The selection of windows and doors should consider energy efficiency, security, and aesthetics.
- Drywall: Drywall is installed on the interior walls and ceilings, creating a smooth and finished surface for painting and wallpaper.
- Flooring: Flooring options include hardwood, tile, carpet, and laminate. The choice of flooring should consider aesthetics, durability, and maintenance requirements.
- Painting: Painting the interior and exterior walls adds color and protection. The choice of paint should consider durability, moisture resistance, and color preference.
- Cabinets and Countertops: Kitchen and bathroom cabinets and countertops provide storage and workspace. The selection of cabinets and countertops should consider aesthetics, durability, and functionality.
Building Codes and Regulations, 4 bedroom slab house plans
Building codes and regulations are designed to ensure the safety, structural integrity, and energy efficiency of buildings. It is crucial to understand and comply with local building codes throughout the construction process.
- Foundation Requirements: Building codes specify the minimum depth and thickness of the slab foundation, as well as the type and amount of reinforcement required.
- Framing Standards: Building codes dictate the size, spacing, and type of lumber used for framing walls and roofs. These standards ensure structural stability and fire resistance.
- Electrical and Plumbing Codes: Electrical and plumbing codes establish standards for wiring, conduit, pipes, and fixtures, ensuring safety and proper functionality.
- Energy Efficiency Requirements: Building codes often include energy efficiency standards, specifying insulation levels, window glazing, and other features that reduce energy consumption.
Selecting Materials and Contractors
Choosing the right materials and contractors is essential for a successful and cost-effective construction project.
- Material Quality: Use high-quality materials that meet building codes and are appropriate for the climate and intended use. This includes lumber, concrete, insulation, siding, roofing, and other materials.
- Contractor Experience: Hire experienced contractors with a proven track record of successful projects. Look for contractors who are licensed, insured, and have positive reviews from previous clients.
- Communication and Collaboration: Maintain clear communication with contractors throughout the project, discussing plans, timelines, and any changes or issues. This ensures a smooth and efficient construction process.
